how to measure cortical thickness|normal cortical thickness of kidney : makers Cortical thickness in neuroimaging is a common measure used to describe the distance between the innermost and outermost edges of the cerebral cortical gray matter (see . WEB14 de out. de 2021 · O chefe de operações de tecnologia Daniel Sturman dá uma espiada por trás das cortinas de nossa Conferência de Desenvolvedores Roblox 2021. Neste .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Eleanor Hibbert grew up in London. She first discovered her fascination for the past when she visited Hampton Court in her teenage years. After her marriage, Hibbert achieved the financial independence she needed to realise her desire to write. London's monuments and royal personalities filled Hibbert's historical novels. She was also influenced by her regular visits to British historic homes a.
The cortical thickness is then calculated at every volumetric point within the cortex and is based on the length of the trajectory from one boundary to another. Here we investigate a method for . There are three classes of techniques for measuring cortical thickness: (1) manual, (2) surface based, and (3) voxel based. Manual measurements rely on the digital .Here, we present an automated method for accurately measuring the thickness of the cerebral cortex across the entire brain, and for generating cross -subject statistics in a coordinate .Thickness, especially cortical thickness, is a widely used metric in MRI, yet there is little in a gold standard to establish its veracity. Common methods (e.g. FreeSurfer) rely on complex .
Cortical thickness in neuroimaging is a common measure used to describe the distance between the innermost and outermost edges of the cerebral cortical gray matter (see . We utilized this BigBrain cortical atlas to test whether previously reported thickness gradients, as measured by MRI in sensory and motor processing cortices, were present in a histological atlas of cortical thickness .
We present a normative dataset of cerebral cortical thickness for human visual areas in a large sample population in the HCP, with the aim of creating a common baseline for . In this work, we present a framework for measuring the cortical thickness, based on minimizing line integrals over the probability map of the gray matter in the MRI volume. We . Nomograms of renal parenchymal thickness, medullary pyramid thickness, renal length, and the ratio of medullary pyramid thickness to parenchymal thickness were de-veloped. When all age groups were pooled together, statistically significant differences were observed between right and left kidneys in terms of parenchymal thickness (p < 0.001), med- cortex thickness equals/is more than 6 mm 14. if the pyramids are difficult to differentiate, the parenchymal thickness can be measured instead and should be 15-20 mm 11. central renal sinus, consisting of the calyces, renal pelvis and fat, is more echogenic than the cortex. renal pelvis may appear as a central slit of anechoic fluid at the hilum
Measurement of cortical thickness index (CTI) and canal flare index (CFI) on an anteroposterior radiograph (using Osirix software). Do: outer diameter (the shaft's outer diameter at 10 cm below the lesser trochanter), Di: inner diameter (the shaft's inner diameter at 10 cm below the lesser trochanter, measured at the same level as Do), CW .The cortical thickness has been used as a biomarker to assess different cerebral conditions and to detect alterations in the cortical mantle. In this work, we compare methods from the FreeSurfer software, the Computational Anatomy Toolbox (CAT12), a Laplacian approach and a new method here proposed, based on the Euclidean Distance Transform (EDT), and its corresponding .These differences in clustering results are attributable at least in part to the many methodological differences between the two studies, such as multi-scanner data in the Karama et al. (2009) study, different methods of extraction of the cortical surface and measurement of cortical thickness, and different techniques to control p-values over . The normal cortical thickness is 7-10 mm; reduced cortical thickness may indicate progressive kidney disease or decreased eGFR. 11, 15, 16 With respect to volume, the normal range in men is 110-190 mL and in women is 90-150 mL. 17 It is possible to measure volume by simplifying the kidney’s shape as spherical or ellipsoid and measuring .
(A) Mean cortical thickness was calculated for the left and right hemispheres independently for each subject, and the difference (left – right) taken as indicator of hemispheric bias. (B) Mean cortical thickness bias across participants and 95% confidence intervals on the mean show areas that significantly deviate from hemispheric symmetry.
why is cortical thickness important
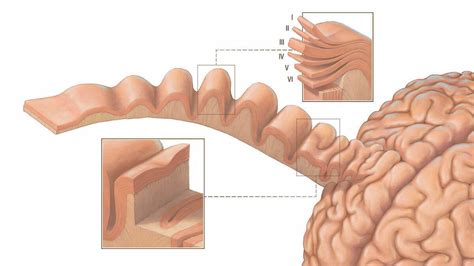
what does cortical thickness indicate
Cortical thickness. The thickness at each vertex is computed as the average of two distances (Fischl and Dale, 2000; Greve and Fischl, . Figure 2: A 3D diagram with the proposed solution to measure the cortical volume. In the surface representation, the cortex is limited internally by the white and externally by the pial surface (a). Cortical thickness and sulcal depth calculated by the Euclidean distance should scale as the 1/3 power of ICV, and cortical surface area as the 2/3 power. . Discrepancies in findings may be attributable to different levels in the measurement of cortical thickness. We used mean cortical thickness in the whole cortex and each lobar region .
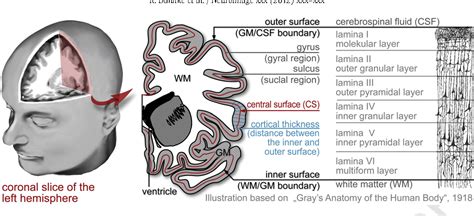
Cortical thickness should be estimated from the base of the pyramid and is generally 7–10 mm. If the pyramids are difficult to differentiate, the parenchymal thickness can be measured instead and should be 15–20 mm ( Figure 3 ) [ 6 ].
Cortical thickness in neuroimaging is a common measure used to describe the distance between the innermost and outermost edges of the cerebral cortical gray matter (see Fig. 1).This can then be used to describe an average thickness for the entire brain (i.e., global), or it can be localized (i.e., local) to different regions of interest (e.g., dorsolateral prefrontal . Laplace methods [Haidar and Soul,2006; Jones et al.,2000; Yezzi and Prince,2003] solve Laplace's equation in the GM region with the boundary condition of constant (but different) potentials on each of the two surfaces.The cortical thickness is then defined at each point as the length of the integral curve of the gradient field passing through that point, as .OBJECTIVE. The objective of our study was to develop, by use of ultrasound, nomograms of renal parenchymal thickness, medullary pyramid thickness (height), renal length, and the ratio of medullary pyramid thickness to parenchymal thickness in healthy children. SUBJECTS AND METHODS. This prospective study included 292 consecutive children (136 boys and 156 girls) .
This page describes the workflow to extract freesurfer cortical thickness values for a region-of-interest (ROI) defined in volume space. For this workflow, assume the following data is present: 1) An ROI mask in the form of a volume file, where the voxel value is '1' in the ROI, and '0' elsewhere. The coordinate space of that volume is irrelevant. The study confirms that the nodal cortical thickness correlates well with the presence of disease. It is easy to measure and appears to be a reliable indicator. Further, the minimum cortical thickness for positivity (27 mm) will help us . Key Points • Evaluation of enlarged lymph nodes with ultrasound includes assessment of size, shape, echogenicity, borders, and vascularity. In general, normal-sized lymph nodes are <1 cm, but size varies by location in .
There was a significant decline in creatinine clearance in subjects who were >60 years of age compared to those <30 years (100 vs. 135 ml/min, respectively, p < 0.005) but without a corresponding reduction in renal length (10.5 vs. 10.75 cm, respectively, p = 0.47; table 2).Similarly, the reduction of cortical thickness with age was not statistically significant (0.89 . 1. INTRODUCTION. Cortical thickness has been used as a very important morphological trait in many brain studies. For instance, global thinning of the cerebral cortex was reported in middle aged humans. 1 Some brain diseases such as Alzheimer are known to cause atrophy in both regional and global cortical regions. 2 There have been studies measuring . In addition, focusing on the joint analysis of thickness and area, we compare an improved, analytic method for measuring cortical volume to a permutation-based nonparametric combination (NPC) method. We use the methods to analyze area, thickness and volume in young adults born preterm with very low birth weight, and show that NPC analysis is a .
The cortical thickness has been used as a biomarker to assess different cerebral conditions and to detect alterations in the cortical mantle. . Surface- and voxel-based methods have advantages and drawbacks regarding computational demands and measurement precision, while thickness definition was mainly associated to the cortical thickness . Logically, changes in cortical volume must be due to changes in either cortical thickness or surface area, or both. Cortical thickness is thought to reflect dendritic arborisation and pruning (Huttenlocher, 1990), while surface area may reflect folding and gyrification, both of which depend on division of progenitor cells in the periventricular area during embryogenesis .Abstract. The distribution of cortical bone in the proximal femur is believed to be a critical component in determining fracture resistance. Current CT technology is limited in its ability to measure cortical thickness, especially in the sub-millimetre range which lies within the point spread function of today’s clinical scanners. For example, a complete labeling of a human brain from a high-resolution T1-weighted MRI scan can take a trained anatomist days to complete, and even this labor-intensive procedure allows only the measurement of cortical volume, not cortical thickness. This difficulty arises because the thickness of the cortex is a property that can only be .
In the study by Bedi et al., cortical morphologic features of nodes were shown to be more reliable predictors of malignancy compared to the size, shape, or echogenicity of the nodes. 5 Normal axillary nodes should have a thin hypoechoic cortex measuring 3 mm or less in thickness, with a central fatty hilum and smooth margins or gentle cortical .
Three separate measurements (A, B, and C) were made with sufficient magnification to measure renal cortical thickness. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS ver. 21 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). RCT, renal length, and eGFR values were measured at the beginning and at the end of the study and were compared using the paired-samples t test dear all, Please let introduce myself: my name is Antonio II, and Im new in worlds measuring by software. I was heard about ImageJ just some weeks ago while Im looking for some video tutorials on Youtube. I was marvelled with such usabillities. But I don’t know how to start about measuring epithelium thickness. Well, I know. Cortical thickness is an important biomarker for image-based studies of the brain. A diffeomorphic registration based cortical thickness (DiReCT) measure is introduced where a continuous one-to-one correspondence between the gray matter–white matter interface and the estimated gray matter–cerebrospinal fluid interface is given by a diffeomorphic mapping in the .

normal cortical thickness of kidney

Rubber Flex Cracking Tester services
Der er gennem vores analyser af udbydere fremhævet fem af de bedste slot casinoer, der opfyldte alle krav for at blive betragtet som et top casino for spillere, der ønsker at spille online slots. Nogle af disse sider er specialiserede i . Ver mais
how to measure cortical thickness|normal cortical thickness of kidney